Dogs are often beloved family companions, providing affection, companionship, and joy. However, interactions between children and dogs, even those considered friendly or familiar, occasionally lead to bites, posing significant health risks. Dog bite infections, particularly in children, are of great concern due to their potentially severe health consequences and the unique susceptibility of young individuals.
Children’s natural curiosity, combined with their limited awareness of danger signs from animals, frequently puts them at increased risk. Understanding why children are more susceptible to infections from dog bites and adopting preventive strategies is essential for parents, caregivers, and pet owners. Recognizing these risk factors can empower adults to take proactive measures to safeguard children’s health.
Physical Vulnerability of Children
Children possess more delicate and thinner skin, along with smaller and less-developed muscles and bones compared to adults. These physiological differences result in dog bites causing more profound and extensive tissue damage in children, which increases the risk of infection. Their immune systems also tend to be less mature, making it harder for them to combat bacteria introduced during animal bites.
Moreover, children’s smaller stature makes their faces, necks, and hands more accessible to biting dogs. These areas of the body contain vital structures such as blood vessels, nerves, and sensory organs that are particularly prone to severe injury and infection.
Severe complications, including nerve damage or infections that can spread rapidly into deeper tissues, are significantly more likely in these sensitive regions. Children’s anatomical vulnerabilities heighten the risks associated with dog bites, emphasizing the need for caution and preventive measures.
Bacteria in Dog Bites
Dog bites introduce harmful bacteria into the skin, increasing the risk of serious infections. Common bacteria found in dog mouths include:
- Pasteurella – A leading cause of painful swelling and skin infections.
- Streptococcus – Can result in cellulitis, abscesses, or systemic infections.
- Staphylococcus – May cause severe skin infections, including antibiotic-resistant strains like MRSA.
- Capnocytophaga – Particularly dangerous for individuals with weakened immune systems, potentially leading to life-threatening complications.
Children are especially vulnerable, as their developing immune systems may struggle to fight infections effectively. Without prompt treatment, these bacterial infections can escalate, leading to hospitalization and long-term health concerns.
Behavioral Factors
Children’s behaviors and interactions with dogs play a significant role in their increased risk of bites and subsequent infections. Young children often struggle to interpret a dog’s body language, which makes it difficult for them to recognize subtle signs of stress, discomfort, or aggression. Unintentional provocation can occur when children approach dogs during mealtime, pull their fur, or hug too tightly, leading to defensive bites.

To reduce the likelihood of bites, educating children about proper interactions and understanding canine behaviors is vital. Teaching them to recognize warning signs of potential aggression can create safer environments during encounters with dogs.
Implementing role-playing scenarios and facilitating supervised interactions with calm, trained dogs can reinforce these lessons. Such approaches promote safe and respectful relationships between children and dogs, ultimately contributing to better understanding and fewer incidents.
Delayed Treatment
Dog bite infections often worsen due to delays in seeking medical help. Children might hesitate to report bites immediately due to fear, embarrassment, or a lack of understanding about the injury’s seriousness. This lag allows harmful bacteria the opportunity to multiply, increasing the infection’s severity and complexity.
It is essential for adults to encourage open communication with children. Creating an environment where kids feel safe to report any animal bites or injuries promptly can help mitigate the risks associated with such incidents.
Seeking immediate medical assessment after any dog bite, regardless of how minor it appears, is crucial. This proactive approach minimizes infection risks and helps prevent potential complications like cellulitis, abscess formation, or systemic infections. In severe cases, legal support from the highest-rated Los Angeles personal injury law firm, Rose, Klein & Marias LLP, can help families handle complex medical and legal challenges following dog bite incidents.
Prevention Strategies
Prevention serves as the most effective strategy to reduce the risk of dog bite infections in children. Supervised interactions between children and dogs, especially for younger kids with unfamiliar animals, are crucial. Teaching children to stay away from unknown dogs and emphasizing the importance of seeking adult assistance during animal interactions can significantly decrease bite incidents.
Responsible pet ownership also plays a vital role in prevention efforts. Ensuring that dogs receive regular veterinary care, vaccinations, training, and proper socialization lowers the chances of aggressive behavior.
Educating parents, caregivers, and dog owners on how to recognize dog behaviors indicative of stress or discomfort creates safer environments for children. Understanding these signs fosters better supervision and interaction, ultimately promoting safer relationships between children and dogs.
When to Seek Medical Help
Dog bites can lead to infections and serious complications, making timely medical attention essential. Seek medical care immediately if:
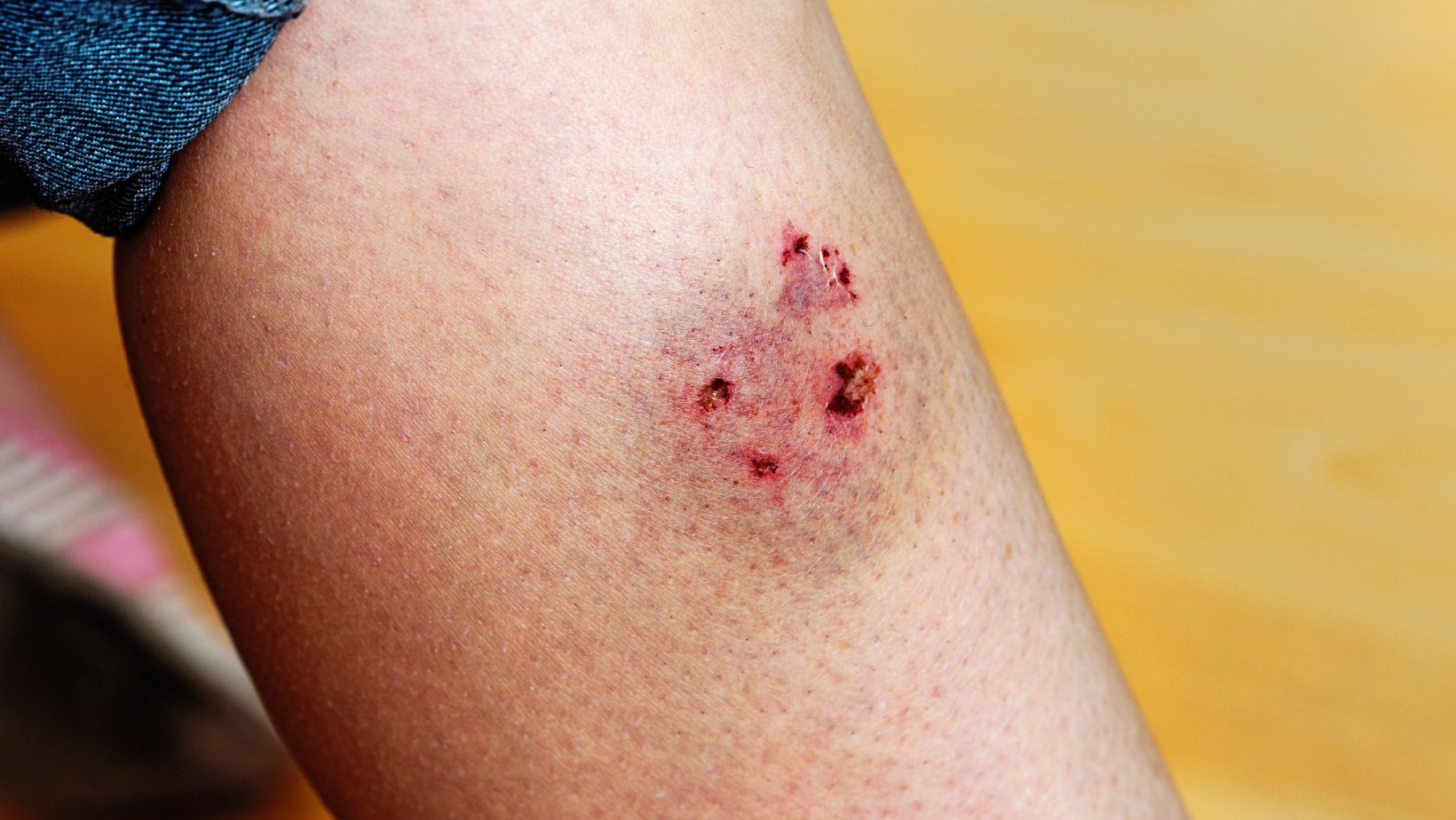
- The bite punctures or significantly breaks the skin – Deep wounds are more prone to infection.
- Signs of infection appear – Swelling, redness, warmth, discharge, or increasing pain at the wound site.
- Systemic symptoms develop – Fever, chills, lethargy, or unusual behavior may indicate a spreading infection.
- The bite is on the face, hands, or joints – These areas are more vulnerable to complications.
- The person bitten has a weakened immune system – Higher risk of severe infections.
Prompt medical intervention helps prevent serious health risks and ensures proper wound care for a safer recovery.
Ensuring Child Safety Around Dogs
Understanding why children are particularly susceptible to dog bite infections highlights the importance of preventive strategies and immediate response measures. By educating children on safe interactions, promptly addressing bites, and promoting responsible pet ownership, adults can significantly mitigate infection risks, ensuring safer and healthier environments for children.
Through increased awareness, proactive measures, and timely intervention, communities can minimize the occurrence and severity of dog bite injuries and infections, safeguarding the health and well-being of children effectively.
